Photo by Michael Dziedzic on Unsplash
How to Create, Read, Update and Delete SQL record with Python Flask
Introduction
We'll be building a simple backend application that creates, reads, update and deletes fruits and it's description in a SQL database with Python Flask.
Getting Started
I expect you have the below listed installed already in your PC
VsCode
Python
PostgreSQL
Postman
Note: You can use other Code Editors , SQL Dialects and API testing tools but this is what i'll be using in this lesson, So now we are good to go yeah?
You can download vs-code Here, Python Here, PostgreSQL Here and Postman Here.
Setting up Virtual Environment
I always recommend creating a virtual environment whenever you want to start a new python project, this helps to keep dependencies required by different projects separate, You can create that easily with the python -m virtualenv venv
Now you'll activate the virtual environment with this command source venv/Scripts/activate
Note: the
venvis the name of the virtual environment, i assume we can proceed now.
Dependencies
We'll need to install flask micro framework and flask_sqlalchemy
flask
flask_sqlalchemy
psycopg2
we can install these dependencies by using the pip install command i.e. pip install flask to install flask
Now let's move on.
Setting up codebase
The First thing you want to do is create a file where your code will be written, let's name it app.py
In the project terminal you can use touch app.py to create the file.
Importing Dependencies
We'll import Flask, request and jsonify from flask and SQLAlchemy from flask_sqlalchemy
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy
Create Flask Instance
Now we'll create Flask Instance and name it app
app = Flask(__name__)
Now the next thing you want to do when you've set your pgAdmin up is create a database the name of my database is hayley
Connect postgres database
The next thing you want to do is connect the postgres database we'll be doing it this way
app.config['SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI'] = 'postgresql://[Username]:[Password]@[Host]:[Port]/[Database name]'
Username = the default username is postgres
Password = it can be set blank if you didn't create any
Host = default is localhost
Port = default is 5432
Database name = the new database i created was named hayley.
Bind the SQLAlchemy instance to flask app
Now the next thing we want to do is binding the SQLAlchemy instance to the flask app this way
db = SQLAlchemy(app)
Create a Fruit model
We want to create a simple table that contains fruits and it's description. We'll create the id which is an integer, name and description which are strings as seen below and then commit the transaction using db.session.commit()
class Fruit(db.Model):
id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True)
name = db.Column(db.String(), nullable=False)
description = db.Column(db.String(), nullable=False)
Now lets's start our Flask App with this command below
export FLASK_APP=app
export FLASK_ENV=development # enables debug mode
python3 app.py
Create a table in the Database
Now we wan't to create the table in our Database with the commands below, you can comment this immediately you create your table.
db.create_all()
db.session.commit()
And your table should look like this in the Database when you run the select * from "fruit" in query tool

Creating a new record
To create a new record we'll name an endpoint /new-fruit with the POST method, a new variable name to get the name of the fruit from the json we'll be using in postman, another variable description to get the description of the fruit and a variable fruit which is an instance of the Fruit model that will be stored in the database. Now we'll add the fruit by using the SQLALchemy db.session.add(fruit) as seen below and then commit the transaction using db.session.commit() .
@app.route("/new-fruit", methods=["POST"])
def new_fruit():
name = request.get_json()['name']
description = request.get_json()['description']
fruit = Fruit(name=name, description=description)
db.session.add(fruit)
db.session.commit()
return jsonify("New Fruit created")
This is the new fruit we'll be adding from our Postman
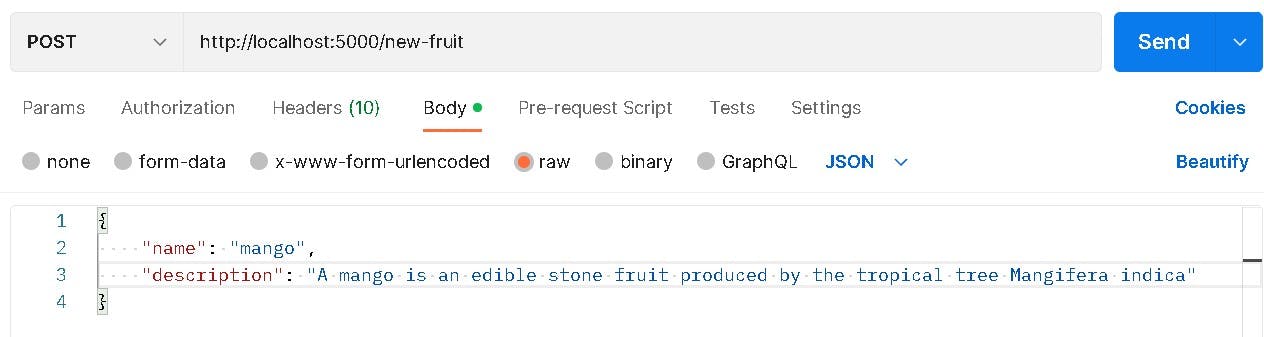
And Our Fruit is now added into the table as seen below.

Get A Record
The next method we'll be using is the GET method, we want to get all fruits in the table, the first thing we'll be doing is define a list named all_fruits then get all fruits with SQLALchemy Fruit.query.all() and assign it to fruits variable, then iterate through all the fruits and append an object that contains fruit.name and fruit.description into the all_fruits list as seen below then return it in JSON format as seen below.
@app.route("/fruits", methods=["GET"])
def get_fruits():
all_fruits = []
fruits = Fruit.query.all()
for fruit in fruits:
all_fruits.append({
"name": fruit.name,
"description": fruit.description
})
return jsonify(all_fruits)
this is how we'll be getting it from Postman
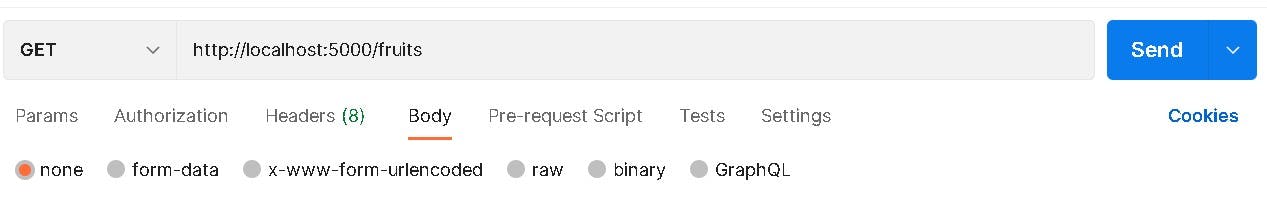
And this is the response we get since we only have one fruit and it's description in the table.

Update A Record
The next method we want to use is the PATCH method, we'll be using it to update an existing fruit's name or it's description. The first thing we'll be doing is to get the particular fruit with SQLALchemy Fruit.query.get(id) containing the id of the fruit, then get both the name and description the same way we did in POST request and then assigned fruit.name to the new name and fruit.description to the new description and then committing the transaction using db.session.commit()
@app.route("/update-fruit/<int:id>", methods=["PATCH"])
def update_fruit(id):
fruit = Fruit.query.get(id)
name = request.get_json()['name']
description = request.get_json()['description']
fruit.name = name
fruit.description = description
db.session.commit()
return jsonify("Fruit Updated Successfully")
We'll be Updating the name from Postman as seen below
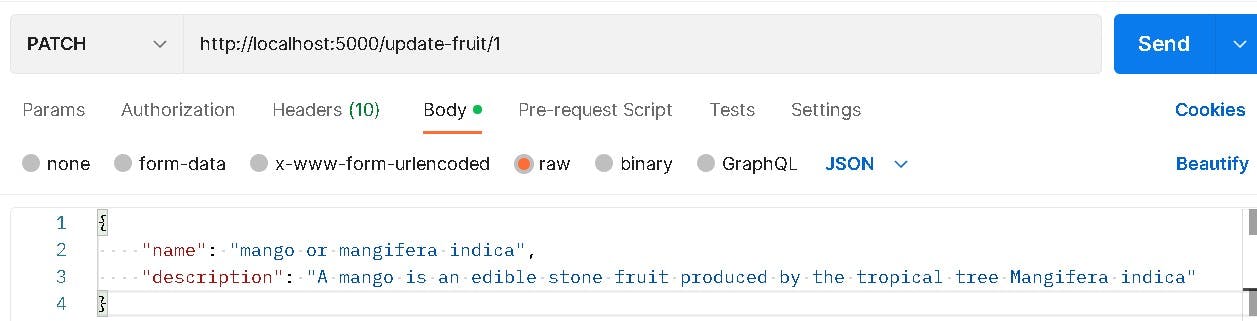
And it should update in our table instantly
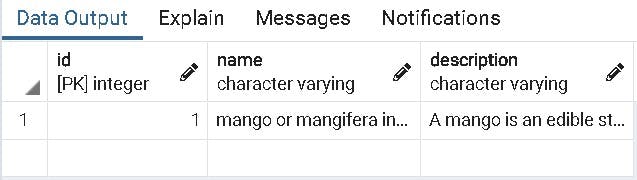
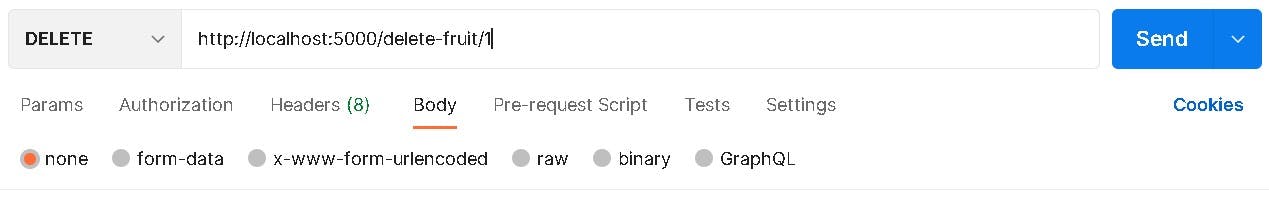
Delete A Record
The Last method we'll be using is the DELETE method, we'll be using this to delete a fruit and it's description. The first thing we'll be doing is to get the particular fruit using SQLALchemy Fruit.query.get(id) then use db.session.delete(fruit) with the fruit instance in the delete() method, then we'll be commiting the transaction using db.session.commit()
@app.route("/delete-fruit/<int:id>", methods=["DELETE"])
def delete_fruit(id):
fruit = Fruit.query.get(id)
db.session.delete(fruit)
db.session.commit()
return jsonify("Fruit Deleted Successfully")
When we call the delete fruit endpoint with the id of the fruit as seen below/delete-fruit/1
The table should be empty as seen below

You can get the complete code for the project Here
Follow me for more backend tips.
